Generative A (GenAI)I, in just a short span of two years, has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to reshape industries ranging from entertainment to healthcare. Capable of creating new content, enhancing decision-making, and optimizing complex processes, GenAI is not only a significant technological advancement but a catalyst for innovation across sectors.
Despite its transformative potential, the market remains in its early adoption stages, facing challenges that need to be addressed for seamless integration. Insights from ISG’s State of the Generative AI Market report reveal that this market is poised for substantial growth and disruption. Here, we explore generative AI’s trends, opportunities, challenges, and its future trajectory.
Introduction to Generative AI
At its core, Generative AI uses algorithms to create original content by learning from existing data, generating text, images, music, and video with a high level of sophistication. Key technologies such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformer models, like OpenAI’s GPT series, have played pivotal roles in expanding generative capabilities.
The essential components of generative AI include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Critical for generating and interpreting human language.
- Computer Vision: Enables the creation of realistic images and videos.
- Reinforcement Learning: Facilitates the development of adaptive systems that learn from their environments.
- Data Augmentation: Expands training datasets, improving model efficacy.
Current Market Landscape
Growth Projections
ISG, which named Emagia a “Rising Star” in its 2024 Provider Lens Finance and Accounting Platforms report, predicted spending will rise by 50% in 2025 compared with 2024. With advancements in cloud computing and processing power lowering entry barriers, it is now accessible to a broader range of businesses. Analysts project the market could surpass $100 billion in the near term, fueled by robust investment from both startups and established corporations.
Industry Adoption
Generative AI has applications across numerous sectors, each harnessing its potential to drive efficiency and innovation. Early adoption trends include:
- Manufacturing: Optimizing design processes and supply chain logistics.
- Finance: Supporting AR, risk management, and fraud detection.
- Healthcare: Applications in drug discovery and personalized medicine.
- Media and Entertainment: Enhancing content creation in areas like scriptwriting and animation.
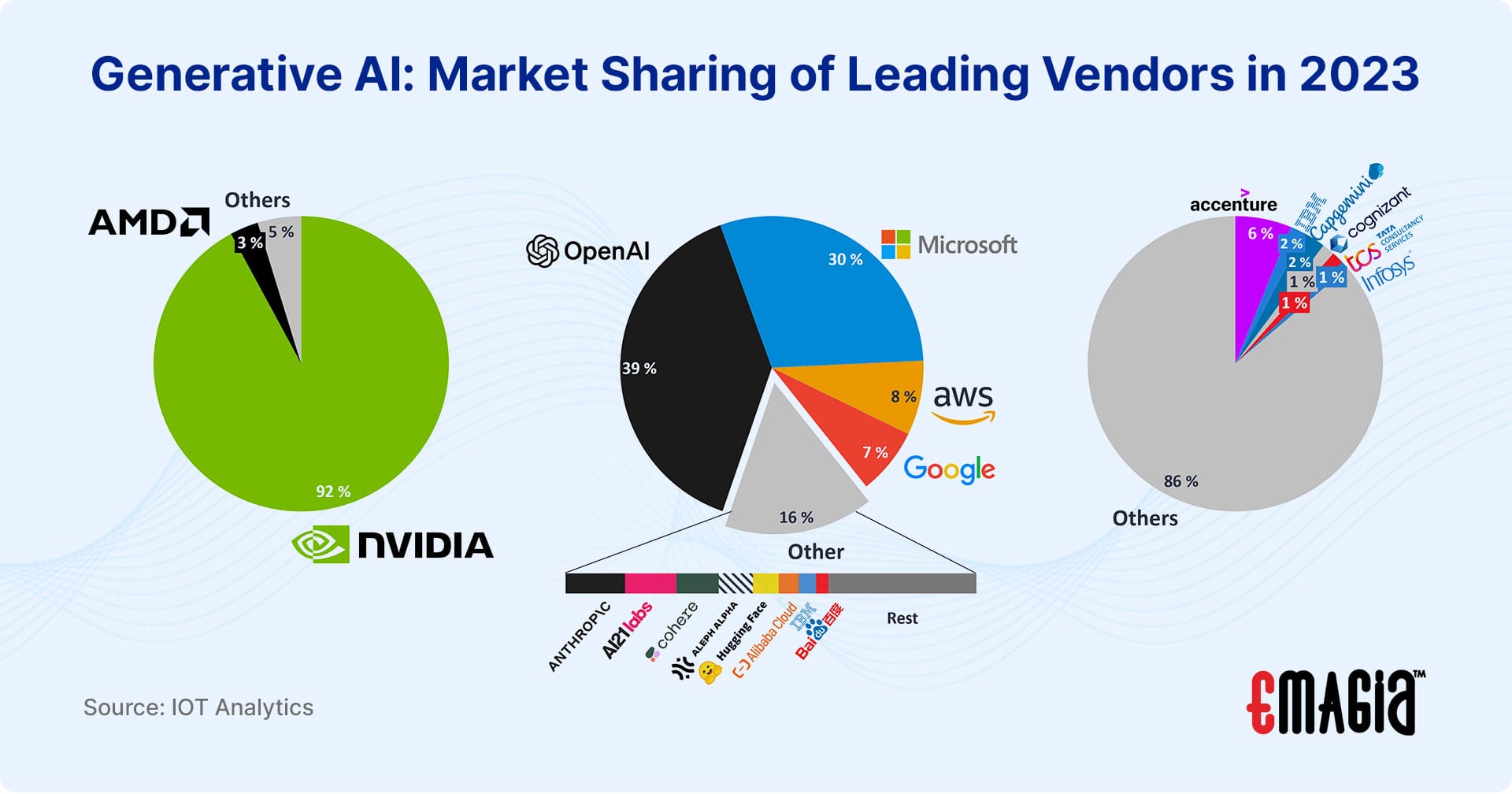
Competitive Landscape
The generative AI landscape is a mix of tech giants and agile startups. Major players, including OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, Meta, and IBM, are investing heavily in the field, while startups focus on niche applications. This competitive environment fosters innovation but also brings challenges related to market saturation and differentiation. Factors impacting the competitive landscape include high entry barriers due to the specialized inputs (e.g., data, computing power, and talent) required and significant regulatory costs, particularly in regions like Europe.
Key Trends Shaping the Market
Several key trends are driving the generative AI market, including:
- Integration with Existing Systems For businesses, generative AI’s value lies in its ability to enhance existing processes. Integrating AI models with current IT infrastructures, primarily ERP systems, allows companies to improve productivity without overhauling their systems.
- Enhanced Collaboration Between Humans and AI Generative AI is designed to augment, not replace, human creativity (Hence the popular “copilot” and “digital assistant” terms). Collaborative tools are emerging that enable real-time interaction between humans and AI, establishing a new paradigm of human-AI synergy.
- Data Privacy & Regulation The rapid adoption of generative AI has prompted concerns around data privacy. Companies are increasingly prioritizing transparency, fairness, and accountability, aligning with emerging regulatory guidelines to promote responsible AI use.
- Democratization of AI Tools User-friendly, no-code, and low-code platforms are opening generative AI to a broader audience, empowering non-technical users to build AI-driven solutions.
Opportunities for Businesses
Innovation in Product Development
Generative AI provides businesses with a unique avenue to innovate product development by simulating scenarios and generating design prototypes, thereby accelerating time-to-market and reducing costs.
Personalized Customer Experiences
Companies can leverage generative AI to create customized customer interactions, from tailored marketing to personalized recommendations, enhancing engagement and customer loyalty.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
By automating content creation and data analysis, generative AI streamlines workflows, reducing the need for manual effort and allowing human resources to focus on strategic activities.
New Revenue Streams
Generative AI is opening new business models and revenue opportunities, including subscription-based AI tools, consulting services, and innovative products rooted in generative capabilities.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its immense potential, generative AI faces several critical challenges:
- Data Quality and Bias: The effectiveness of GenAI depends on the quality of the data it is trained on. Bias or poor-quality data can result in inaccurate or ethically problematic outputs, raising important considerations for responsible AI use. That’s part of why Emagia designed its answer to ChatGPT for finance and credit-related purposes, dubbed GiaGPT, is a “closed-cloud” solution where users upload data – which is not shared – they want used.
- Technical Complexity: Implementing GenAI requires specialized expertise, as well as resources to integrate it with existing systems. High computational demands add another layer of complexity. This is why so many companies are looking into expanded training, or “upskilling”, for their staff.
- Rapidly Evolving Landscape: Generative AI is developing at a fast pace, and companies must remain agile to stay competitive and leverage the latest advancements.
- Perception and Trust: Trust and acceptance will play a pivotal role in generative AI’s future. Transparency, and clear communication are essential to foster a positive perception of generative AI’s role within a business and to garner “buy-in” from those ultimately tasked with using AI-based solutions to drive enhanced efficiency and profitability.
Future Directions
Advancements in Technology
Future advancements in AI technology will bring about more sophisticated generative models and multimodal capabilities, allowing businesses to create richer content across different formats, from text and images to audio and video.
Increased Collaboration and Open-Source Initiatives
Collaboration among tech companies, researchers, and governments is essential to address generative AI’s challenges. Open-source platforms will democratize technology, making it accessible to smaller firms and fostering innovation across industries.
Expansion of Use Cases
As technology advances, generative AI’s applications will broaden, with industries like education, legal services, and agriculture poised for innovative use cases.
Conclusion
The generative AI market stands at a transformative juncture. Technological advancements and increasing adoption suggest vast opportunities ahead for businesses seeking to innovate and enhance efficiency. However, successfully navigating the complexities and ethical considerations of generative AI will be essential for long-term success. As the interplay between human creativity and AI continues to evolve, GenAI almost certainly will define the next wave of innovation, reshaping industries and setting new standards for productivity and creativity in the digital age.
FAQ
Who Is ISG?
ISG (Information Services Group) is a leading global technology research and advisory firm. A trusted business partner to more than 900 clients, including more than 75 of the world’s top 100 enterprises, ISG is committed to helping corporations, public sector organizations, and service and technology providers achieve operational excellence and faster growth. The firm specializes in digital transformation services, including AI, cloud and data analytics; sourcing advisory; managed governance and risk services; network carrier services; strategy and operations design; change management; market intelligence and technology research and analysis.
What is the ISG Provider Lens Finance and Accounting Platforms Report?
ISG’s Provider Lens™ Finance and Accounting Platforms report evaluates 22 providers across two quadrants: Invoice to Cash (I2C) and Record to Report (R2R). Emagia’s recognition as a “Rising Star” in the I2C quadrant reflects its strong portfolio and high potential for continued success in the finance and accounting SaaS market.